Phonetic and phonological contrast: digraphs ch, ll, sh, rr in English, Spanish, and Kichwa
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69850/rimi.vi3.173Palabras clave:
kichwa, phonetics, phonologyResumen
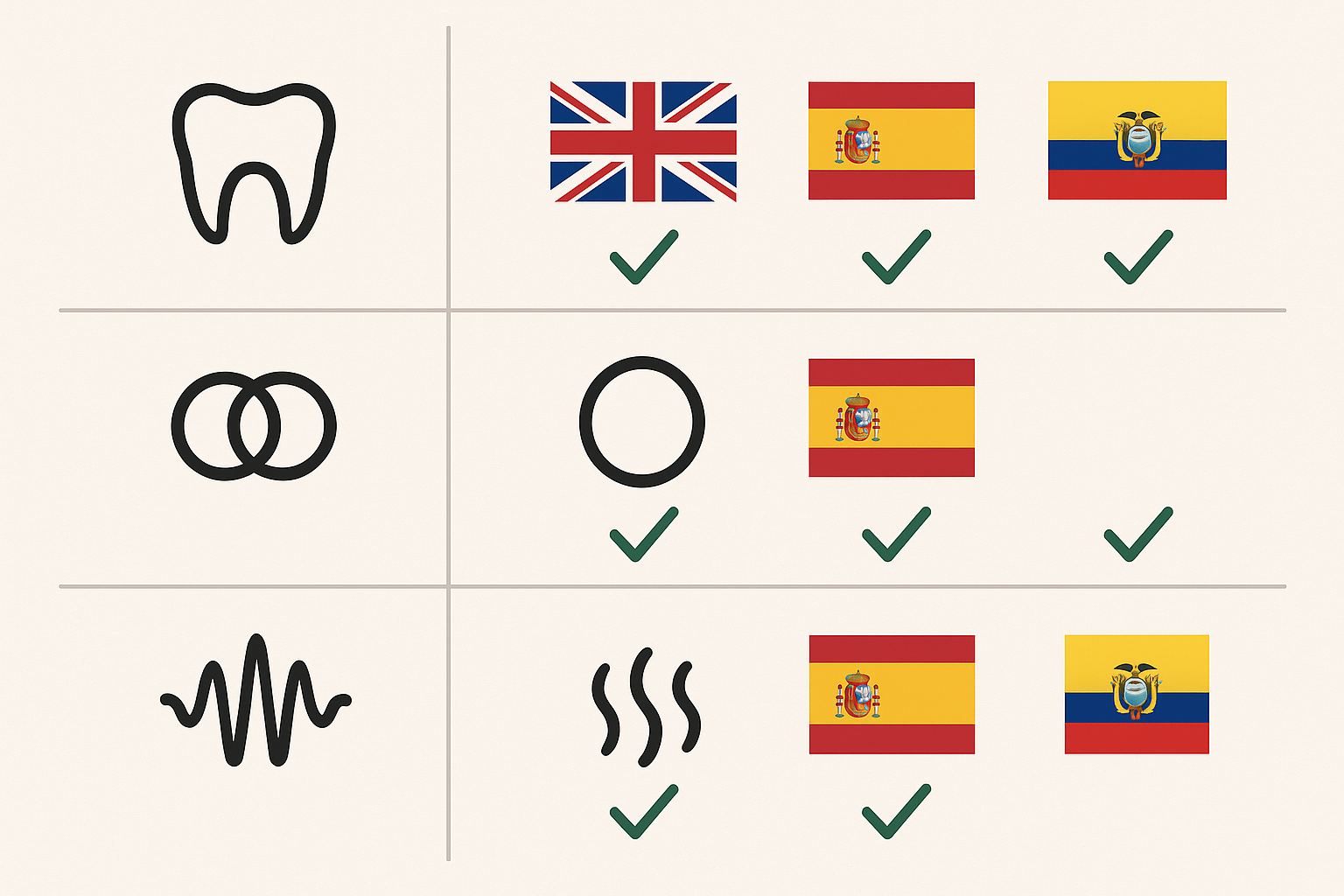
This research examined the phonetic and phonological contrast of the digraphs ch, ll, sh, and rr in English, Spanish, and Kichwa among Kichwa-speaking students at Yachay Tech University. A qualitative methodology was employed, applying document analysis, participant observation, and interviews as data collection methods. Based on the population size, a census sample equivalent to the total population was used, consisting of seventeen Indigenous students from Yachay Tech. Once the data had been collected, an in-depth phonetic and phonological analysis of Kichwa words and phrases was conducted. The results revealed that the Kichwa language contained more allophones of both vowel and consonant sounds compared to English and Spanish. Furthermore, through the phonetic and phonological distribution of the digraphs ch, ll, sh, and rr in Spanish, English, and Kichwa, two types of distribution were identified: total and partial. Total occurred when a phoneme or allophone appeared in initial, medial, and final positions; partial occurred when a phoneme or allophone did not appear in all positions. Finally, through the analysis of contrastive transfer between the languages, English and Spanish, English and Kichwa, and Spanish and Kichwa, two types of transfer were identified: positive and zero. Positive transfer occurred when the sound of a phoneme or an allophone was very similar in both languages, while zero transfer occurred when specific sounds were present in only one language and absent in the others.
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 René Mauricio Matabay Cargua , Elma Elvira Quinde Robles , Jeannette Solayda Torres Guerrón

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.


